While it has been long acknowledged that obesity is an epidemic in America, many insurers are refusing to cover the prescribed medications to help those who are struggling. The Food and Drug Administration has approved highly effective anti-obesity medications, but they are not covered by insurance.
These insurance companies claim that weight loss medications are not necessary pharmaceuticals and are merely for the user’s vanity. This creates a loophole for insurers, who deny coverage for those medicines.
This has led many who need the medications for their health and well-being to be unable to afford them. Without insurance coverage, people can’t always pay out of pocket for a costly drug.
We explain why most insurers do not cover weight loss medications below.
Table Of Contents
Toggle- What are Common Weight Loss Medications?
- Saxenda Weight-Loss Pens
- How do Anti-Obesity Medications Work?
- What are the Side Effects of Anti-Obesity Medicines?
- Who Should Take Anti-Obesity Medications?
- Why do Doctors Prescribe Weight Loss Medications?
- Vanity Medications or Healthcare?
- Why Don’t Insurers Cover Weight Loss Medications?
- Conclusion
What are Common Weight Loss Medications?
The FDA has approved a handful of weight loss medications for long-term usage, including Contrave, Saxenda, Xenical, Qsymia, and Wegovy. However, this newest class of anti-obesity medications is highly effective in combating obesity, weight loss, and reversing obesity-related issues.
Saxenda
The FDA has recently approved Saxenda to fight obesity. In trials, Saxenda was highly effective in helping participants lose weight, improve their blood sugar, and decrease their risk of heart disease. Diabetes can also be managed with this daily shot. Saxenda was created by Novo Nordisk and has been compared to Ozempic. Similar to Ozempic, both are not covered by most healthcare insurers.
To avoid paying premium dollar, many Americans buy Saxenda from Canada, as their prices are much cheaper.
Wegovy
Wegovy is another new class of anti-obesity medications with mounting evidence of effectiveness and safety. It helps with weight loss and obesity management and is also prescribed to treat type 2 diabetes. Users take Wegovy as a weekly shot.
Contrave
Contrave is a combination of two medications; Bupropion, which is commonly used as an anti-depressant and an aid to stop smoking, and Naltrexone, which is used to treat various addictions. Together, the two work cohesively to help with weight loss.
Xenical
Xenical has had many success stories when helping users lose weight. It is a medication called Orlistat with a reduced-strength, over-the-counter option called Alli.
Qsymia
A combination of weight loss medication Phentermine and anticonvulsant medication Topiramate, Qsymia is effective in fighting obesity. However, there are multiple potential side effects of Phentermine, including misuse, high heart rate, and insomnia.
Saxenda Weight-Loss Pens
$514.99How do Anti-Obesity Medications Work?
The new highly safe and effective anti-obesity medications include Saxenda, Wegovy, among others. These medicines work in several ways. They suppress the users’ appetite to aid in weight loss. They are most effective for losing weight when paired with diet and exercise.
Many weight loss medications are also used as a treatment for type 2 diabetes. The hormone mimics GLP-1, which tells the pancreas to produce more insulin, which controls blood sugar.
These anti-obesity medications are also believed to slowly empty the stomach, stopping people from eating sooner and feeling full for more extended periods. This prevents overeating which aids in the loss of weight for obese patients.
What are the Side Effects of Anti-Obesity Medicines?
Most weight loss medications share similar side effects, such as stomach pain, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.

Some medications also have more severe and uncommon side effects, such as liver injury, high blood pressure, suicide risk, insomnia, constipation and other similar symptoms. Symptoms vary from case-by-case, but a thorough examination (including your family history) should be conducted before being placed on any medication.
You should speak to your healthcare provider immediately if you think you’re experiencing any side effects when taking these medications. Furthermore, the drug must be taken for an extended period. Some weight loss medicines are for long-term use, while others are merely short-term. Taking medications longer than intended can increase serious side effects and cause complications.
Who Should Take Anti-Obesity Medications?
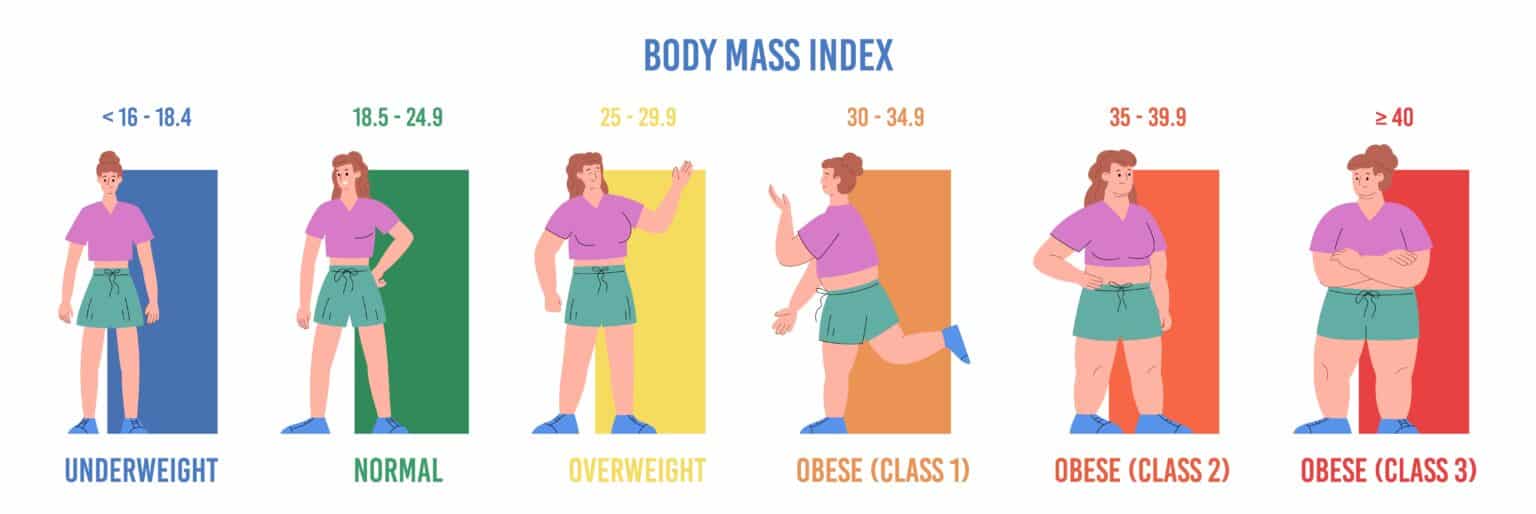
There are some basic qualifications for taking medications, although each has its requirements. Over 30 is considered obese by most anti-obesity doctors. They can also be prescribed to those with a BMI in the high 20s if they have other risk factors, such as diabetes or heart disease.
Why do Doctors Prescribe Weight Loss Medications?
Many modern weight loss medicines have been used for years to treat type 2 diabetes. Eventually, doctors began to notice that their patients were losing weight when using them. This caused drug makers to start offering higher medications to treat obesity. As trials were run and patients began using the medicine for weight loss, it became apparent that they were highly effective.
Nearly two-thirds of the adult population is overweight and obese. With so many patients needing weight loss, doctors are happy to prescribe effective medications that serve a dual purpose; helping their patients lose weight and experience relief for several weight-related conditions.
Doctors prescribe these medications to help with weight loss and other obesity-related issues. These issues include blood sugar, heart disease, and more.
These medications are now FDA-approved and can seamlessly be prescribed by a physician to aid in losing weight. Doctors have begun to see the multiple benefits of these medications and regularly prescribe them to their patients.
The effectiveness of these medications makes them an excellent option for patients who are obese or overweight. Most patients who use these anti-obesity medications lose over 20% of their weight over 72 weeks. Doctors who are seeking options and help for their obese patients find these medications to be a viable and successful choice.
Vanity Medications or Healthcare?
Unfortunately, many insurance companies won’t cover even when doctors prescribe anti-obesity medications for weight loss and other weight-related conditions. Instead of viewing weight loss medications as healthcare, they consider them vanity medications.
Older weight loss drugs were thought of as cosmetic treatments. They didn’t have the results current medications have, and they were often found unsafe.
The designation of weight loss medications as vanity drugs comes from the perpetuating falsehood that obesity is all about bad choices. However, there is a large percentage of obesity risk inherited.
Due to their safety and weight loss effectiveness, their treatment of conditions associated with weight loss, and the fact that obesity is a disease, anti-obesity medications should be viewed as a form of healthcare rather than vanity.
Why Don’t Insurers Cover Weight Loss Medications?

About one-third of insurance companies don’t cover any form of weight loss medications, while another third only cover those that are FDA-approved. This is problematic as most anti-obesity medications are costly, and most patients cannot purchase them out of pocket. Most obese Americans are on the lower income end of the spectrum, creating another hurdle for these people as they attempt to get healthy.
Aside from the designation of weight loss medication as a vanity drug, there are other reasons that many insurers don’t cover them. Traditionally, weight loss medications have been unsafe and caused numerous health issues for users. Old drugs such as Fen-phen had to be pulled due to the discovery that they caused damaged heart valves in users.
Another reason insurers are hesitant about covering weight loss medications is the possibility that users will remain on them for their lives. In this instance, the cost to insurance companies would be enormous.
Conclusion
Doctors regularly prescribe weight loss medications for obese and overweight patients. These medications have a high effectiveness rate and help with other weight-related conditions.
Unfortunately, many insurance companies don’t cover these medications, leaving those who need them most incapable of accessing them. They don’t cover them because they consider them cosmetic or vanity drugs instead of healthcare. They also feel they are unsafe and ineffective.
With obesity playing such a massive role in the lack of health in America, people must have access to anti-obesity medications. Hopefully, insurance companies will soon rethink their position on these medications so that those who need them can use them, lose weight, and get healthy.
Share: